What Is Project Quality Control
What Is Project Quality Control
In this article, we will explore the concept of project quality control. Whether you are a project manager or simply interested in understanding more about project management, this article will provide valuable insights into how quality control plays a crucial role in the success of any project. We will delve into the importance of project quality control, its key principles, and how it relates to project management, programme management, and the agile methodology. By the end of this article, you will have a better understanding of what project quality control entails and its significance in ensuring project success. So, let’s dive into the world of project quality control and unlock the keys to effective project management.
Speak to MCTC today about our consultancy advice and training packages.

What is project quality control?
Project quality control refers to the processes and activities that are implemented to ensure that a project meets the defined quality standards. It involves systematically reviewing and evaluating the various components of a project to ensure that they adhere to the established quality criteria. Project quality control is an essential aspect of project management as it helps to identify any potential quality issues and take corrective actions to ensure that the project delivers the desired outcomes.
Importance of project quality control
Project quality control is crucial for the successful completion of a project. Here are some reasons why it is important:
- Customer satisfaction: By implementing effective quality control processes, you can ensure that the final deliverables of the project meet the expectations of the customer. This leads to higher levels of customer satisfaction and increases the likelihood of repeat business or positive referrals.
- Risk mitigation: Quality control helps to identify and address any potential risks or issues that may arise during the project. By addressing these issues proactively, you can minimise the impact of risks on project outcomes and ensure smooth project execution.
- Cost savings: Implementing robust quality control processes can help in identifying and rectifying quality issues at an early stage. This prevents costly rework or late-stage changes, resulting in cost savings for the project.
- Reputation management: Delivering high-quality projects enhances the reputation of the project team and the organisation as a whole. A track record of successful projects completed to high standards can attract more clients and opportunities for future business.
Key principles of project quality control
To ensure effective project quality control, it is necessary to adhere to some key principles. These principles serve as guidelines for implementing quality control processes in a systematic and efficient manner. Here are three key principles of project quality control:
Defining quality objectives
Before embarking on any quality control activities, it is important to define clear and measurable quality objectives. Quality objectives should align with the overall project goals and should be specific, achievable, relevant, and time-bound. These objectives will provide a framework for assessing the quality of deliverables and guiding the quality control efforts throughout the project.
Identifying quality standards
To ensure that project deliverables meet the required level of quality, it is essential to identify and define the applicable quality standards. These standards can be internal, such as organisational policies and procedures, or external, such as industry guidelines or regulatory requirements. By clearly defining the quality standards, project teams can evaluate whether the deliverables meet the desired level of quality.
Establishing quality control processes
Establishing robust quality control processes is critical for implementing effective project quality control. This involves defining the specific activities, techniques, and tools that will be used to monitor and evaluate the quality of project deliverables. Quality control processes should be integrated into the overall project management plan and should be consistently applied throughout the project life cycle.
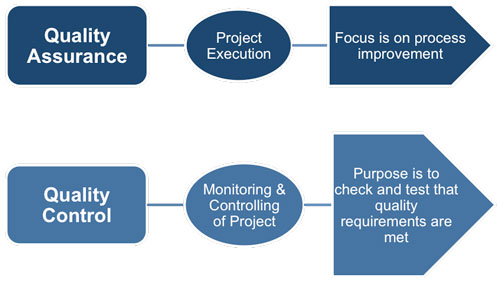
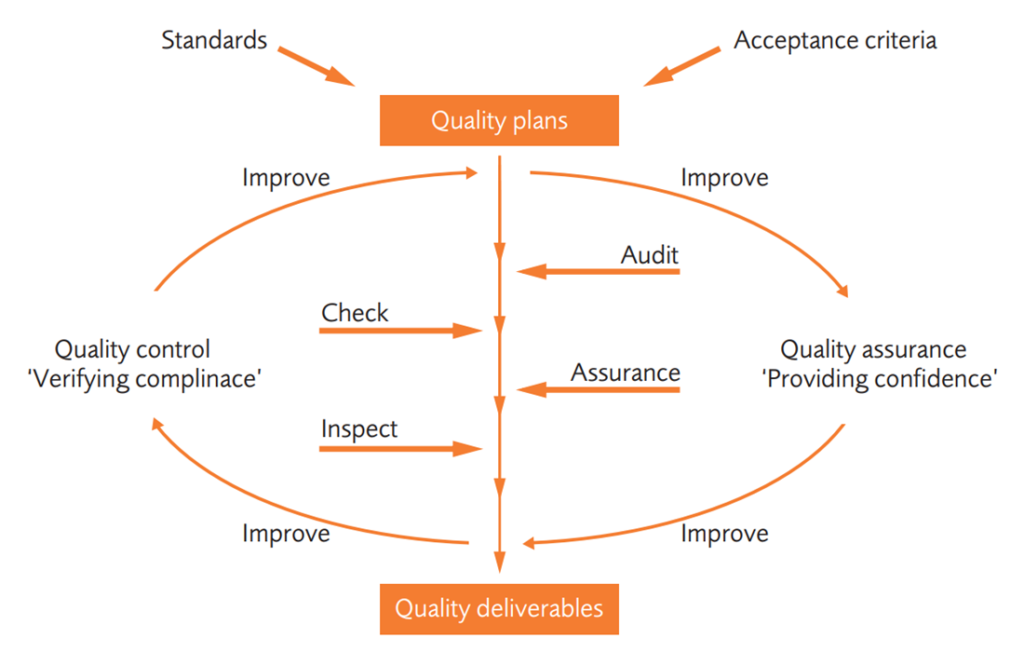
Project quality control vs. project quality assurance
While project quality control and project quality assurance are both essential aspects of project management, they differ in terms of their focus and objectives.
Project quality control primarily focuses on the monitoring and evaluation of project deliverables to ensure that they meet the defined quality standards. It involves activities such as inspections, reviews, and tests to identify and rectify any quality issues.
On the other hand, project quality assurance focuses on the processes and systems that are established to ensure that the project is being executed in accordance with the defined quality standards. It involves activities such as establishing quality management plans, conducting audits, and implementing corrective actions to prevent quality issues from arising in the first place.
Both project quality control and project quality assurance are essential for achieving project success. While quality control focuses on the outputs of the project, quality assurance focuses on the processes and inputs to ensure the outputs are of high quality.
The role of project managers in quality control
Project managers play a crucial role in ensuring effective project quality control. Here are some key responsibilities of project managers in quality control:
Setting quality expectations
As leaders of the project team, project managers are responsible for setting clear quality expectations for the project. This involves communicating the quality objectives and standards to the team members and other stakeholders. By clearly communicating the desired level of quality, project managers help create a shared understanding and commitment towards delivering high-quality outcomes.
Creating quality management plans
Project managers are responsible for creating quality management plans that outline the processes and activities for quality control. These plans include details of the quality control processes, the roles and responsibilities of team members, and the techniques and tools to be used for evaluating quality. By creating comprehensive quality management plans, project managers ensure that quality control efforts are well-documented and systematically implemented.
Monitoring and evaluating quality
Project managers play a key role in monitoring and evaluating the quality of project deliverables. This involves conducting regular inspections, reviews, and tests to ensure that the deliverables meet the defined quality standards. Project managers also analyse quality control results and take appropriate actions to rectify any identified issues. By actively monitoring and evaluating quality, project managers ensure that quality control efforts are effectively implemented throughout the project.
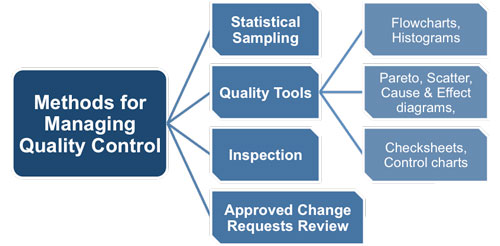
Tools and techniques for project quality control
To carry out effective project quality control, project teams can utilise various tools and techniques. Here are four commonly used tools and techniques for project quality control:
Checklists and templates
Checklists and templates provide a structured approach to quality control. They help in ensuring that all necessary quality control activities are carried out systematically and consistently. Checklists are used to verify that specific requirements are met, while templates provide standardised formats for documenting quality control results.
Statistical sampling
Statistical sampling is a technique used to evaluate the quality of a project deliverable by examining a representative sample. It involves randomly selecting a subset of the deliverables and assessing their quality. The results obtained from the sample can then be extrapolated to the entire population of deliverables, providing an estimate of the overall quality.
Process analysis
Process analysis involves examining the project processes and workflows to identify areas where quality improvements can be made. This technique helps in uncovering any bottlenecks or inefficiencies that may affect the quality of the project deliverables. By analysing the processes, project teams can implement corrective actions to enhance the quality of the project.
Risk analysis
Risk analysis is an important tool for assessing the potential risks that may impact the quality of a project. It involves identifying and analysing risks that may arise during the project and evaluating their potential impacts on the quality of deliverables. By conducting risk analysis, project teams can develop mitigation strategies to minimise the impact of risks on project outcomes.
Steps in project quality control
Implementing project quality control involves several steps that need to be followed systematically. Here are the five steps in project quality control:
Identifying quality control activities
The first step in project quality control is to identify the specific activities that are required to monitor and evaluate the quality of project deliverables. This involves reviewing the quality objectives and standards and determining the appropriate activities based on the project requirements. Examples of quality control activities include inspections, reviews, tests, and audits.
Assigning responsibilities
Once the quality control activities have been identified, the next step is to assign responsibilities to the appropriate team members. Each quality control activity should have a designated team member responsible for its execution. Assigning responsibilities ensures accountability and helps in ensuring that all necessary quality control activities are carried out as planned.
Executing quality control activities
After assigning responsibilities, the identified quality control activities need to be executed. This involves conducting inspections, reviews, tests, and other relevant activities as per the defined quality management plan. During the execution phase, project teams should follow the specified processes and use the designated tools and techniques for evaluating the quality of project deliverables.
Evaluating quality control results
Once the quality control activities have been executed, the next step is to evaluate the results. This involves analysing the findings from inspections, reviews, tests, and other quality control activities. The results are compared against the defined quality objectives and standards to assess the level of compliance. Any identified issues or deviations are documented and appropriate actions are taken to address them.
Common challenges in project quality control
While project quality control is essential for project success, there are several common challenges that project teams may face. Here are four common challenges in project quality control:
Lack of clarity in quality requirements
One of the common challenges in project quality control is the lack of clarity or ambiguity in the quality requirements. If the quality requirements are not well-defined, it becomes difficult to assess the quality of project deliverables accurately. To address this challenge, project teams should invest time upfront in clearly defining the quality objectives and standards, and ensure that all stakeholders have a shared understanding of the requirements.
Insufficient resources for quality control
Another challenge is the lack of sufficient resources, such as time, budget, and skilled personnel, for quality control activities. Insufficient resources can hinder the effective implementation of quality control processes, leading to compromised quality. To overcome this challenge, project teams should allocate adequate resources for quality control and prioritise quality as a key aspect of the project.
Resistance to change
Implementing effective project quality control may require changes to existing processes or practices. Resistance to change from team members or stakeholders can pose a challenge to the successful implementation of quality control processes. To address this challenge, project managers should actively communicate the benefits of quality control and involve team members in the change process to gain their support and buy-in.
Inadequate communication and collaboration
Effective communication and collaboration are crucial for project quality control. Lack of communication or collaboration among team members can lead to miscommunication, misunderstanding, and ultimately compromised quality. To overcome this challenge, project teams should establish clear channels of communication, encourage collaboration and teamwork, and foster a culture of open and transparent communication.
Best practices for effective project quality control
To ensure effective project quality control, project teams should follow some best practices. Here are four best practices for effective project quality control:
Engaging stakeholders in quality control
Engaging stakeholders in quality control activities can help ensure that their expectations and requirements are considered in the quality control processes. By involving stakeholders from the early stages of the project, project teams can gain valuable insights and feedback, leading to better quality outcomes.
Continuously improving quality control processes
Project teams should embrace continuous improvement in their quality control processes. This involves regularly evaluating the effectiveness of the current processes, identifying areas for improvement, and implementing necessary changes. Continuous improvement helps in enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of quality control efforts, leading to improved project outcomes.
Ensuring sufficient training and development
Providing sufficient training and development opportunities to team members is essential for effective project quality control. By equipping team members with the necessary knowledge and skills, they can execute their quality control responsibilities more effectively. Training can include topics such as quality management techniques, quality control tools, and relevant industry standards.
Embracing a proactive approach to quality control
Taking a proactive approach to quality control can help identify and address quality issues proactively before they escalate. This involves conducting regular risk assessments, fostering a culture of quality, and promoting open communication within the project team. By being proactive, project teams can minimise the impact of quality issues and ensure a higher level of quality in project deliverables.
Conclusion
Project quality control is a critical aspect of project management that ensures project deliverables meet the defined quality standards. By implementing effective quality control processes, project teams can enhance customer satisfaction, mitigate risks, and achieve cost savings. Project managers play a key role in setting quality expectations, creating quality management plans, and monitoring and evaluating quality. Various tools and techniques, such as checklists, statistical sampling, process analysis, and risk analysis, can be utilised for project quality control. While there may be challenges in implementing quality control, following best practices such as engaging stakeholders, continuously improving processes, providing sufficient training, and embracing a proactive approach can contribute to effective project quality control. By prioritising quality and investing in quality control efforts, project teams can enhance project outcomes and contribute to the success of the organisation.