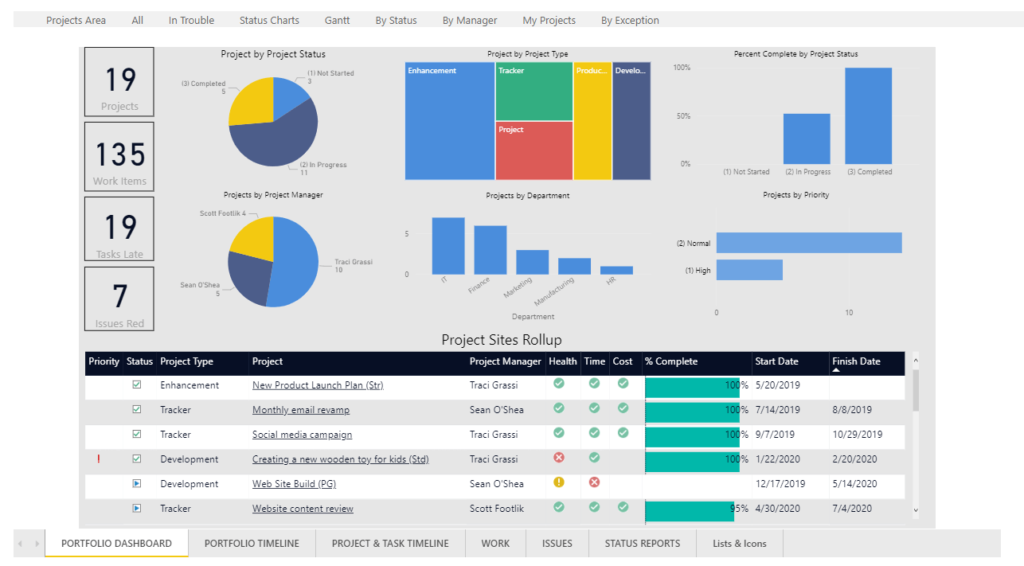
Project Management Reporting
Project Management Reporting
In the world of project management, reporting plays a crucial role in keeping stakeholders informed about the progress, challenges, and outcomes of a project. Whether you’re a project manager yourself or just curious about the inner workings of project management, understanding project management reporting is essential. This article aims to provide you with insights into this topic, exploring the importance of project management reporting, its various components, and how it can help in ensuring successful project delivery. So, let’s dive into the world of project management reporting and discover what it entails.
Speak to MCTC today about our consultancy advice and training packages.

Understanding Project Management Reporting
What is project management reporting?
Project management reporting is the process of collecting, analysing, and presenting data and information regarding the progress, status, and performance of a project. It involves summarising relevant data and presenting it in a clear and concise manner to stakeholders, team members, and other interested parties. Project management reporting provides insights into the project’s progress, identifies any risks or issues, and facilitates effective decision-making.
Importance of Project Management Reporting
Effective communication and transparency
Project management reporting plays a crucial role in facilitating effective communication and promoting transparency throughout the project life cycle. It provides a platform for project managers and team members to share progress, challenges, and achievements with stakeholders. By regularly communicating through project management reports, everyone involved in the project is able to understand the current status, contributing to a more collaborative and cohesive working environment.
Monitoring project progress
One of the primary purposes of project management reporting is to monitor the progress of a project. Through status reports, progress reports, and other forms of reporting, project managers are able to track the completion of project tasks, milestones, and deliverables. This allows them to identify any deviations from the original plan and take necessary corrective actions to keep the project on track.
Identifying and addressing risks
Project management reporting also helps in identifying and addressing risks that may arise during the course of a project. By including risk reports in project management reports, project managers can assess potential risks, evaluate their impact on the project, and develop appropriate mitigation strategies. This ensures that risks are proactively managed, minimising their negative impact on the project’s success.
Resource allocation and budget management
Another important aspect of project management reporting is resource allocation and budget management. By including information on resource utilisation and allocation, project managers can ensure that the necessary resources are available to complete the project successfully. Financial reports provide insights into the project’s budget, helping project managers to track expenses, control costs, and make informed decisions regarding resource allocation.
Types of Project Management Reports
Status reports
Status reports provide a snapshot of the project’s current condition and progress. They typically include information on completed tasks, ongoing activities, and upcoming milestones. Status reports help stakeholders stay informed and gauge the project’s overall health and progress.
Progress reports
Progress reports provide an overview of the project’s progress in relation to the original plan. They outline completed tasks, activities in progress, and any delays or issues encountered. Progress reports are valuable in assessing whether the project is on track and meeting its objectives.
Financial reports
Financial reports provide information on the project’s budget, expenses, and financial performance. They help project managers and stakeholders monitor and control costs, ensure budgetary compliance, and make informed decisions regarding financial resource allocation.
Risk reports
Risk reports focus on identifying potential risks and outlining mitigation strategies. They highlight risks that may impact the project’s success and provide insights into actions being taken to address them. Risk reports ensure that project teams are prepared for potential challenges and can take proactive measures to prevent or minimise their impact.
Quality reports
Quality reports focus on monitoring and evaluating the quality of deliverables and work processes within the project. They assess adherence to quality standards, highlight any deviations or non-compliance, and suggest improvements for maintaining or enhancing quality.
Stakeholder reports
Stakeholder reports provide information specifically targeted at project stakeholders. They summarise the project’s progress, risks, issues, and achievements, with a focus on addressing the concerns and interests of the stakeholders. Stakeholder reports ensure that stakeholders are kept informed and engaged throughout the project.
Key Components of Project Management Reports
Project background and objectives
Every project management report should start with a clear description of the project’s background, objectives, and scope. This provides context and helps stakeholders understand the purpose and desired outcomes of the project.
Summary of activities completed
A comprehensive project management report should include a summary of the activities that have been completed since the previous report. This allows stakeholders to track progress and evaluate the project’s timeline and milestones achieved.
Milestones and deliverables achieved
Highlighting milestones and deliverables achieved is essential to showcase the progress made in a project. Project management reports should clearly outline the key milestones and deliverables that have been accomplished, providing a sense of accomplishment and demonstrating progress towards project goals.
Issues and challenges faced
It is important to capture and document any issues or challenges that the project team has encountered. This provides transparency and allows stakeholders to understand the obstacles that may be impacting the project’s progress. By outlining these issues, project managers can also seek support and input from stakeholders to resolve them effectively.
Risks and mitigation strategies
Risks are inevitable in any project, and project management reports should include a section dedicated to identifying and addressing them. This includes a thorough analysis of potential risks, their impact on the project, and proposed mitigation strategies. By proactively addressing risks, project managers can minimise their impact and ensure the project’s success.
Resource utilisation and allocation
Project management reports should provide insights into the utilisation and allocation of project resources. This includes information on the allocation of personnel, equipment, and other resources, ensuring that the project is adequately resourced and that resources are optimised for maximum efficiency.
Budget analysis
Financial aspects are critical in project management, and reports should include a detailed analysis of the project’s budget. This includes tracking expenses, comparing against budgeted amounts, and identifying any significant deviations. Budget analysis ensures that financial resources are effectively managed and that there is sufficient control over project costs.
Performance metrics and KPIs
Project management reports are incomplete without performance metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs). These metrics should align with the project’s objectives and provide insights into the project’s performance against predetermined targets. Performance metrics and KPIs enable stakeholders to assess the project’s success and identify areas for improvement.
Next steps and action plans
Project management reports should include a clear outline of the next steps and action plans for the project. This ensures that stakeholders are aware of the project’s future direction and can provide input or support where needed. The next steps and action plans keep the project moving forward and facilitate effective decision-making.
Recommendations for improvement
To continuously improve project management practices, it is important to include recommendations for improvement in project management reports. These recommendations should be based on lessons learned, identified areas for improvement, and feedback received from stakeholders. By incorporating these recommendations into future projects, organisations can enhance their project management processes and increase the likelihood of project success.
Effective Project Management Reporting Strategies
Clearly define reporting requirements
To ensure effective project management reporting, it is essential to clearly define and communicate reporting requirements to all stakeholders. This includes specifying the frequency, format, and content of reports to be submitted. By providing clear guidelines, project managers can ensure consistency and accuracy in reporting.
Establish a reporting schedule
Regular reporting is vital in project management. Establishing a reporting schedule ensures that reports are submitted on time and that stakeholders are kept informed at regular intervals. The reporting schedule should align with the project’s timeline and take into account the reporting needs of different stakeholders.
Gather accurate and relevant data
To provide meaningful insights, project management reports must be based on accurate and relevant data. Project managers need to establish reliable data collection mechanisms and ensure that data is validated before inclusion in reports. By focusing on accurate and relevant data, project management reports become more reliable and support informed decision-making.
Use visual aids and data visualisation
Project management reports can be enhanced by using visual aids and data visualisation techniques. Visual representations, such as charts, graphs, and tables, help stakeholders understand complex information more easily. This improves the clarity and impact of the reports, making them more effective in conveying key messages.
Maintain consistency in reporting format
To ensure that project management reports are easily understood and consistent, it is important to maintain a standardised reporting format. This includes using consistent terminology, layout, and structure across all reports. Consistency in reporting format facilitates easy comparison and analysis, ensuring that stakeholders can quickly and accurately interpret the information provided.
Ensure clarity and concise communication
Clarity and concise communication are crucial in project management reporting. Reports should be written in a clear and concise manner, using simple language and avoiding jargon. By ensuring that the information is easily understood, project managers facilitate effective decision-making and minimise the risk of misunderstandings.
Regularly review and analyse reports
Project management reports should not only be submitted but also reviewed and analysed on a regular basis. This allows project managers to identify trends, patterns, and areas for improvement. By analysing reports, project managers can gain valuable insights into the project’s performance, make informed decisions, and take corrective actions as necessary.
Share reports with stakeholders
Project management reports are meant to be shared with stakeholders to keep them informed and engaged. It is important to distribute reports to relevant stakeholders in a timely manner. By sharing reports, project managers promote transparency and collaboration, building trust and ensuring alignment among all project stakeholders.
Implement feedback and recommendations
Feedback and recommendations received from stakeholders should be carefully considered and implemented in project management reporting. By acting on feedback, project managers demonstrate their commitment to continuous improvement and stakeholder satisfaction. Implementing recommendations ensures that project management reporting evolves to meet the changing needs of the project and its stakeholders.
Challenges in Project Management Reporting
Incomplete or inconsistent data
One common challenge in project management reporting is the availability of incomplete or inconsistent data. This can happen due to various reasons, such as data entry errors, lack of data collection protocols, or the reluctance of team members to provide accurate information. Project managers need to establish robust data collection processes and ensure data accuracy to address this challenge.
Lack of stakeholder engagement
Another challenge is the lack of stakeholder engagement in project management reporting. When stakeholders are not actively involved in the reporting process, their understanding of the project’s progress and challenges may be limited. Project managers should proactively engage stakeholders and seek their input and feedback to overcome this challenge.
Difficulty in tracking and reporting progress
Tracking and reporting progress accurately can be challenging, especially in large and complex projects. Without proper tools and systems in place, project managers may struggle to capture and update progress in real-time. Implementing project management software and tracking mechanisms can help overcome this challenge and ensure accurate reporting.
Time and resource constraints
Project managers often face time and resource constraints when preparing project management reports. The process of data collection, analysis, and report creation requires significant time and effort. Additionally, resource constraints may limit the availability of skilled staff to work on reporting tasks. Effective resource management and prioritisation are necessary to address these constraints.
Data overload and information fatigue
Project management reporting can sometimes result in data overload and information fatigue. Too much information, presented in a disorganised or unclear manner, can overwhelm stakeholders and make it difficult for them to extract meaningful insights. Project managers should strive to present information in a concise and organised way, focusing on the key messages and providing context when necessary.

Best Practices for Project Management Reporting
Set clear objectives and expectations
Before embarking on project management reporting, it is essential to set clear objectives and expectations. This includes determining the purpose of the reports, the target audience, and the desired outcomes. By setting clear objectives, project managers ensure that the reporting process aligns with the project’s goals and delivers the intended benefits.
Choose appropriate reporting tools and software
Selecting the right reporting tools and software is crucial for effective project management reporting. There are various tools available that can automate data collection, analysis, and report generation, saving time and improving accuracy. Project managers should assess their reporting needs and choose tools that are user-friendly and align with their organisational requirements.
Standardise reporting templates
Standardising reporting templates helps ensure consistency and efficiency in project management reporting. By creating standardised templates, project managers eliminate the need to reinvent the reporting structure for each report. This also makes it easier for stakeholders to navigate through different reports, as they become familiar with the format and structure.
Automate data collection and analysis
Automating data collection and analysis processes can significantly streamline project management reporting. Using project management software and tools, project managers can collect data in real-time, automate calculations and data processing, and generate reports with minimal manual effort. This not only saves time but also reduces the risk of errors associated with manual data handling.
Use real-time reporting dashboards
Real-time reporting dashboards provide stakeholders with up-to-date information on the project’s progress and key performance indicators. These dashboards can be accessed online and are often customisation to meet specific reporting needs. Real-time reporting dashboards allow stakeholders to view the project’s status and performance at any time, facilitating timely decision-making and collaboration.
Regularly communicate with project team
Effective project management reporting requires regular communication with the project team. Project managers should conduct regular meetings or check-ins to gather updates, address questions or concerns, and ensure that the team understands the reporting requirements. This promotes collaboration and ensures that the project management reports accurately reflect the progress and challenges faced by the team.
Provide training on reporting processes
To improve the quality and effectiveness of project management reporting, project managers should provide training on reporting processes to team members. This includes explaining the purpose and importance of reporting, providing guidance on data collection and analysis, and familiarising the team with reporting tools and templates. Training ensures that everyone involved understands their role in the reporting process and can contribute effectively.
Document lessons learned for future projects
Project management reporting is not just about reporting on the current project; it also involves learning from past experiences. Project managers should document lessons learned during the reporting process, highlighting what worked well and areas for improvement. This documentation can serve as a valuable resource for future projects, enabling organisations to continuously evolve and enhance their project management practices.
Project Management Reporting in Agile
Importance of agile reporting
Agile project management methodologies emphasise the importance of continuous feedback and adaptation. Agile reporting enables project managers to gather feedback from stakeholders, update progress in real-time, and make iterative improvements throughout the project. Agile reporting promotes transparency, collaboration, and agility in responding to changing project requirements.
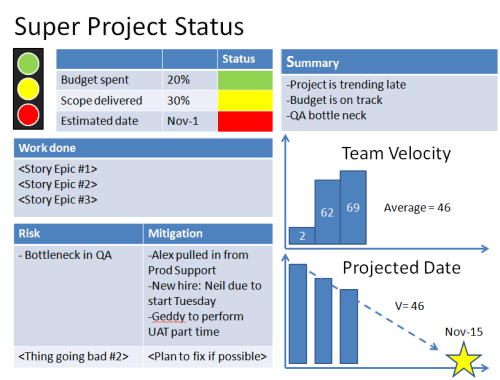
Use of burn down charts and velocity reports
Agile project management often utilises burn down charts and velocity reports to track progress and performance. Burn down charts show the amount of work remaining versus the planned timeline, allowing project managers to assess if they are on track. Velocity reports measure the team’s output and productivity, providing insights into the project’s pace and capacity.
Daily stand-up meetings and progress updates
Daily stand-up meetings are a common practice in agile project management and serve as a form of progress update. These brief meetings allow team members to share what they have accomplished, what they plan to do next, and any challenges they are facing. Daily stand-up meetings contribute to continuous communication and alignment within the team.
Adaptation and flexibility in reporting
Agile project management reporting embraces adaptation and flexibility. Reports should be dynamic and reflect the changing nature of the project. Agile reporting allows project managers to adjust priorities, update progress, and incorporate feedback in real-time. This flexibility enables project teams to respond to emerging challenges and deliver value in an efficient and timely manner.
Collaboration between teams and stakeholders
Agile project management reporting encourages collaboration between project teams and stakeholders. Regular interaction and feedback loops ensure that stakeholders are engaged and have visibility into the project’s progress. Collaboration facilitates consensus-building, reduces the risk of misunderstandings, and helps maintain alignment between the project’s objectives and stakeholder expectations.
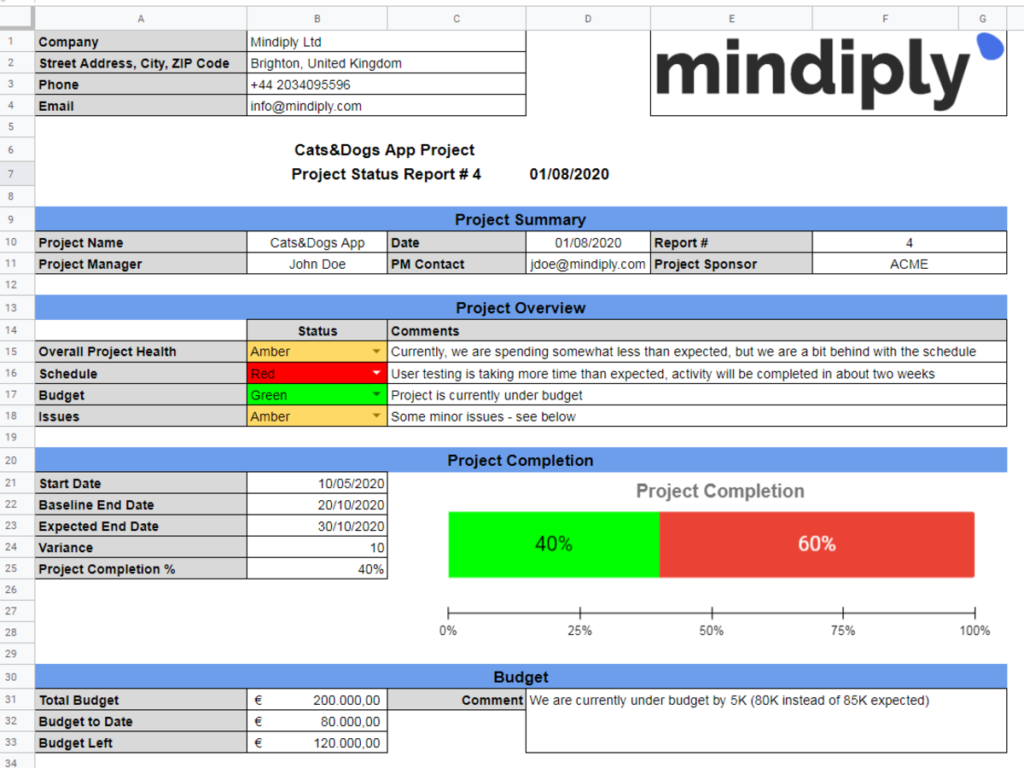
Project Management Reporting vs Programme Management Reporting
Differences between project management and programme management
Project management and programme management are distinct disciplines, although they share similarities in terms of reporting. Project management focuses on managing individual projects, whereas programme management involves managing a group of related projects aimed at achieving a common goal or strategic objective. Programme management reporting typically encompasses multiple projects and focuses on the overall programme’s progress, risks, and performance.
Reporting requirements and scope
Project management reporting focuses on individual project performance, progress, and risks. It provides detailed insights into the status and health of a specific project. Programme management reporting, on the other hand, requires a broader scope and provides a consolidated view of multiple projects within the program. Programme management reports highlight inter dependencies between projects, resource allocation across projects, and the overall achievement of program objectives.
Integration of project and programme reports
The integration of project and programme reports is crucial for effective programme management reporting. Programme management reports should include project-level reports to provide a holistic view of the program’s progress. By integrating project reports, programme managers can identify dependencies, assess overall performance, and make informed decisions at the program level. Integration ensures alignment between projects and program objectives, facilitating effective program management.
Conclusion
Project management reporting is an essential tool for project managers and stakeholders to monitor progress, communicate effectively, and make informed decisions. By understanding the importance of project management reporting and following effective reporting strategies and best practices, organisations can maximise the value of project management reports and increase the likelihood of project success. Whether in traditional project management, agile methodologies, or programme management, effective project management reporting contributes to transparency, collaboration, and the achievement of project objectives.