
Project Management Maturity
Project Management Maturity
In the world of business, project management plays a crucial role in ensuring the success of various initiatives. But what exactly is project management maturity? It refers to the level of competency and effectiveness an organisation has in its project management practices. Whether it’s managing individual projects or overseeing complex programs, having a high level of project management maturity enables businesses to achieve their goals more efficiently, adapt to changes, and deliver value to their stakeholders. In this article, we will delve into the concept of project management maturity, its importance, and how organisations can enhance it to drive success in their projects.
Speak to MCTC today about our consultancy advice and training packages.
Understanding Project Management Maturity
Project management maturity refers to the level of development and effectiveness that an organisation has reached in managing its projects. It signifies the organisation’s capability to consistently deliver successful outcomes, meet stakeholder expectations, and continuously improve its project management practices. In simpler terms, project management maturity is a measure of how well an organisation can plan, execute, and control its projects.
Why is project management maturity important?
Project management maturity is essential for organisations that want to achieve their strategic goals and stay competitive in today’s dynamic business environment. Here are a few reasons why project management maturity is important:
- Effective Resource Allocation: Mature project management practices enable organisations to allocate their resources efficiently. By having a clear understanding of project priorities, capacity, and availability, organisations can make better decisions about resource utilisation, ensuring that the right people are working on the right projects at the right time.
- Improved Decision Making: When project management practices mature, decision making becomes more informed and effective. Mature organisations have established processes for risk management, financial analysis, and project selection, allowing them to make data-driven decisions that minimise risks and maximise return on investment.
- Enhanced Stakeholder Engagement: Mature project management practices focus on engaging stakeholders throughout the project life cycle. By involving stakeholders early on, understanding their needs, and soliciting their feedback, organisations can increase project success rates and maintain strong relationships with their stakeholders.
- Continuous Learning and Improvement: Project management maturity promotes a culture of continuous learning and improvement within an organisation. Mature organisations embrace lessons learned from previous projects, implement best practices, and encourage knowledge sharing among project teams. This continuous improvement mindset leads to enhanced project performance and increased organisational efficiency.
1. Defining project management maturity
Project management maturity can be defined as the progressive development of an organisation’s project management capabilities. It involves the evolution of processes, methodologies, and competencies that enable the organisation to achieve consistent and predictable project outcomes.
1.1 The Project Management Maturity Model (PMMM)
The Project Management Maturity Model (PMMM) is a widely recognised framework that organisations use to assess and improve their project management maturity. Developed by the Project Management Institute (PMI), the PMMM provides a road map for organisations to systematically advance their project management practices.
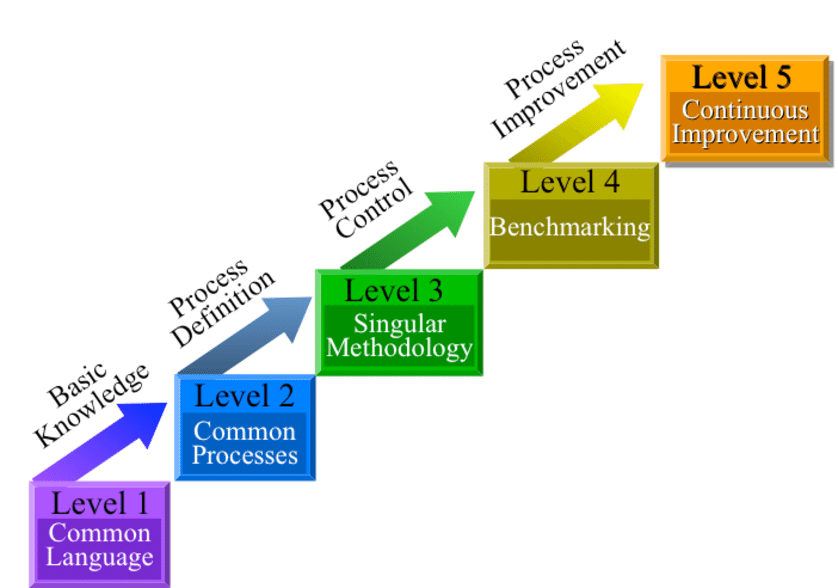
1.1.1 Key components of the PMMM
The PMMM consists of several key components that organisations should focus on to improve their project management maturity:
- Leadership: Leadership plays a crucial role in driving project management maturity. Effective leaders provide the necessary support and resources, set clear expectations, and champion project management initiatives throughout the organisation.
- Methodology and Processes: Organisations need to establish standardised methodologies and processes for managing projects. These methodologies define the steps, tools, and techniques that project teams should follow to ensure consistent and successful project execution.
- People and Skills: Building a skilled workforce is essential for project management maturity. Organisations should invest in training and development programs to enhance the skills and competencies of their project managers and team members.
- Metrics and Measurement: Effective measurement systems enable organisations to track and analyse project performance. By capturing relevant project data and metrics, organisations can identify areas for improvement and make data-driven decisions.
- Continuous Improvement: Project management maturity is a journey of continuous improvement. Organisations should establish mechanisms to capture lessons learned, promote knowledge sharing, and implement feedback loops to enhance their project management practices continually.
1.1.2 Levels of project management maturity
The PMMM defines five levels of project management maturity:
- Level 1: Initial – In this stage, project management processes are ad-hoc and largely undocumented. Project success depends on the skills and abilities of individual project managers.
- Level 2: Repeatable – Organisations at this level have basic project management processes in place but lack consistency and standardisation. Success is reliant on individual project managers following their own methods and practices.
- Level 3: Defined – At this level, organisations have established standardised project management processes and methodologies that are consistently applied across projects. Best practices are documented and shared within the organisation.
- Level 4: Managed – Organisations at this level have a defined project management infrastructure that enables effective project planning, tracking, and control. Project performance is measured and monitored, and corrective actions are taken when necessary.
- Level 5: Optimising – In this final stage, organisations continuously improve their project management practices. They actively seek feedback, monitor industry trends, and drive innovation in project management processes to deliver exceptional results.
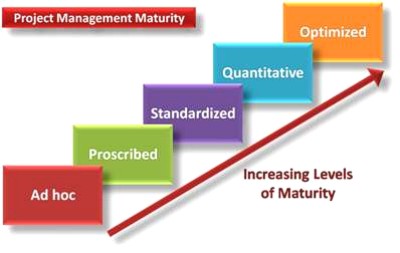
1.2 Other project management maturity models
While the PMMM is widely used, there are also other project management maturity models that organisations can leverage. These models, such as the OPM3 (Organisational Project Management Maturity Model) and CMMI (Capability Maturity Model Integration), offer additional frameworks for assessing and enhancing project management maturity.
OPM3 focuses on the integration of project management practices within the organisation’s overall strategy and operations. It emphasises the alignment of projects with business objectives and the establishment of a project management culture within the organisation.
CMMI, on the other hand, is a comprehensive framework that encompasses project management as well as other organisational processes. It addresses various aspects of organisational maturity, including software development, systems engineering, and service management.
- Assessing project management maturity
To assess project management maturity, organisations can use a combination of self-assessment tools, bench marking, and external audits. These methods help organisations identify their current level of maturity, determine areas for improvement, and develop a road map for enhancing their project management practices.
Self-assessment tools, such as maturity assessment questionnaires, are designed to evaluate an organisation’s project management practices against predefined criteria. These criteria are typically based on the key components of project management maturity and the levels defined by the chosen maturity model.
Bench marking involves comparing an organisation’s project management practices to those of other similar organisations or industry standards. It provides insights into how well the organisation performs compared to its peers and helps identify areas where improvements can be made.
External audits, conducted by independent experts or external consultants, provide an unbiased evaluation of an organisation’s project management practices. These audits offer valuable feedback and recommendations for improving project management maturity.
- Conclusion
Project management maturity is crucial for organisations seeking to achieve project success, maximise resource utilisation, and drive continuous improvement. By following established maturity models like the PMMM, organisations can assess their current level of maturity, identify areas for improvement, and take steps towards advancing their project management practices.
Through effective leadership, standard methodologies, skilled personnel, performance measurement, and a focus on continuous improvement, organisations can gradually increase their project management maturity. This journey towards maturity will result in improved decision making, stakeholder engagement, and overall project success.
As organisations navigate the challenges of managing projects in an ever-changing business landscape, project management maturity becomes a significant differentiator. By investing in maturity, organisations can ensure they are equipped to deliver successful outcomes and drive positive change within their organisations.
So, embrace project management maturity, foster a culture of continuous improvement, and watch your organisation thrive in an increasingly complex and competitive environment.
