
Project Stakeholder Analysis
Project Stakeholder Analysis
In “The Ultimate Guide to Creating a Project Stakeholder Analysis,” you will discover the essential steps and strategies for effectively conducting a stakeholder analysis in your project. Whether you are a project manager, part of a program management team, or interested in agile methodologies, this comprehensive guide will provide you with the insights needed to identify and engage key stakeholders. By understanding their perspectives, interests, and influence, you can ensure the success of your project and build strong relationships with stakeholders along the way. Get ready to unlock the power of stakeholder analysis and take your project management skills to new heights!
Speak to MCTC today about our consultancy advice and training packages.
Understanding Project Stakeholders
Definition of stakeholders
Stakeholders are individuals or groups who have an interest or a stake in a project. They can influence the project and are affected by its outcome. Stakeholders can include anyone from clients and customers to employees, suppliers, investors, and even the local community. They may have different levels of power, influence, and interest in the project.
Importance of stakeholder analysis
Stakeholder analysis is a crucial step in project management as it helps identify and understand the needs, expectations, and concerns of various stakeholders. By analysing stakeholders, project managers can effectively plan and execute projects, make informed decisions, manage risks, and build strong relationships with stakeholders.
Types of stakeholders
There are different types of stakeholders that project managers need to consider:
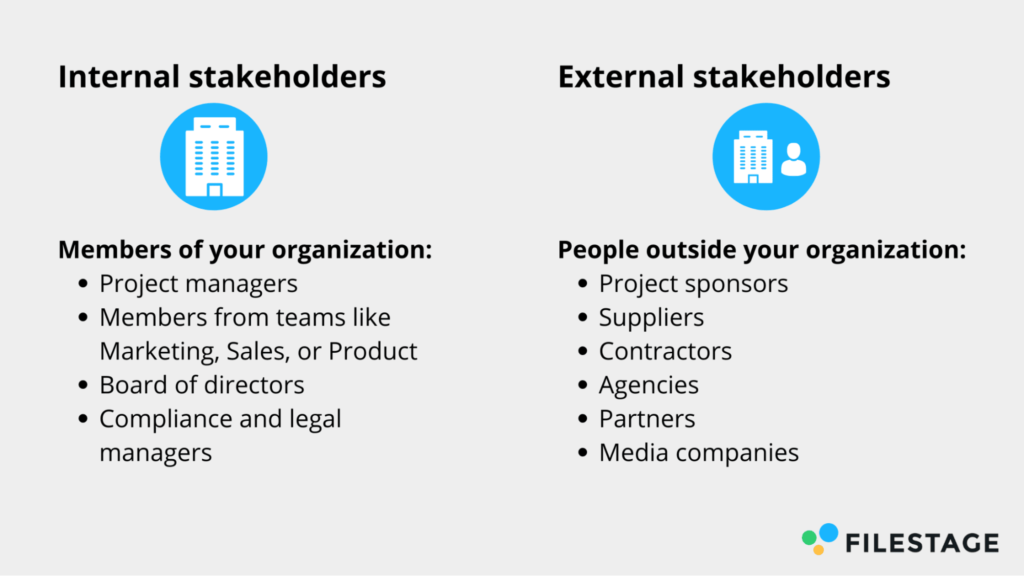
- Internal stakeholders: These are individuals or groups directly involved in the project, such as the project team, management, and employees.
- External stakeholders: These are individuals or groups outside the organisation who have an interest or influence in the project. They can include clients, customers, suppliers, government agencies, and the local community.
- Primary stakeholders: These are stakeholders who are directly affected by the project and have a significant interest or influence in its outcome, such as clients, employees, and investors.
- Secondary stakeholders: These are stakeholders who are indirectly affected by the project, such as the local community or special interest groups. While their influence may be lower, they can still impact the project.
- Key stakeholders: These are stakeholders who have high power and high interest in the project. They often play a crucial role in decision-making and can significantly impact the project’s success.
Benefits of Conducting a Stakeholder Analysis
Identifying key players and decision-makers
Stakeholder analysis helps identify key players and decision-makers within the project. By understanding the roles and influence of different stakeholders, project managers can effectively engage with them, involve them in decision-making processes, and ensure their needs and expectations are met.
Understanding stakeholder interests and objectives
By analysing stakeholders, project managers can gain a deeper understanding of their interests, objectives, and expectations. This knowledge allows project managers to align project goals with stakeholder needs, identify potential conflicts, and find ways to satisfy conflicting interests.
Managing stakeholder expectations
Stakeholder analysis enables project managers to effectively manage stakeholder expectations by identifying and addressing any potential issues or concerns. Understanding the level of influence and interest of different stakeholders helps project managers set realistic expectations and develop appropriate communication and engagement strategies.
Mitigating project risks
Stakeholder analysis helps identify potential risks associated with stakeholders. By understanding their interests, influence, and potential conflicts, project managers can proactively address risks and find ways to mitigate their impact. This allows for better risk management and increases the chances of project success.
Building stakeholder relationships
Stakeholder analysis provides insights into the dynamics and relationships between different stakeholders. This knowledge allows project managers to build effective relationships, establish trust, and foster cooperation among stakeholders. Strong stakeholder relationships enhance collaboration, improve project outcomes, and increase stakeholder satisfaction.
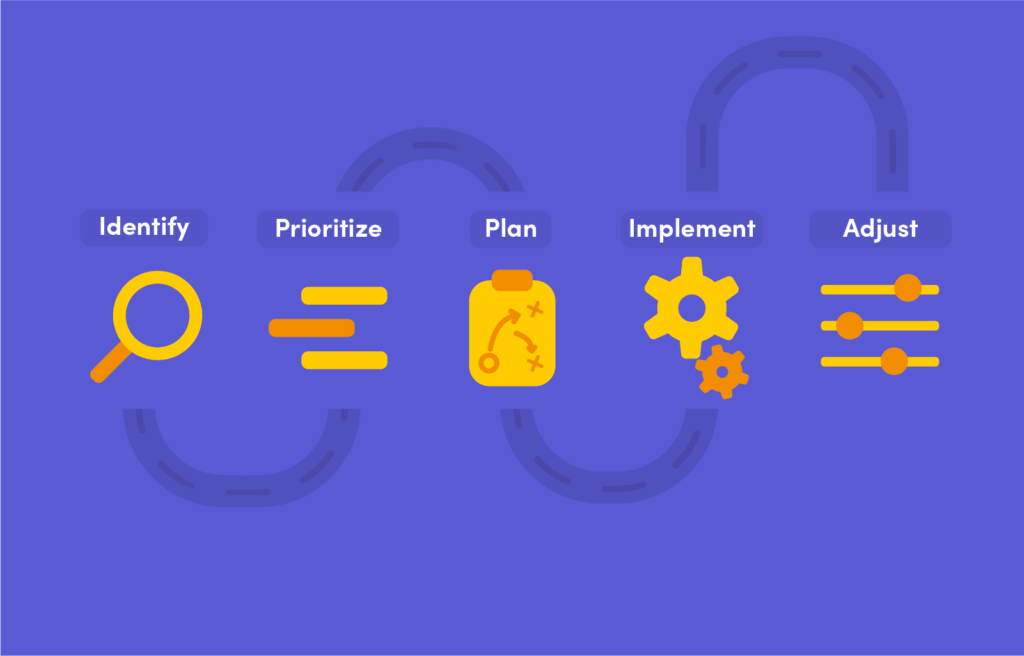
Step-by-Step Guide for Creating a Stakeholder Analysis
Step 1: Identify project stakeholders
The first step in creating a stakeholder analysis is to identify all potential stakeholders. This involves brainstorming and gathering input from the project team, management, and other relevant sources. It is important to consider both internal and external stakeholders and ensure that no stakeholders are overlooked.
Step 2: Determine stakeholder influence and involvement
Once stakeholders are identified, the next step is to determine their level of influence and involvement in the project. This can be done by assessing their power, authority, expertise, and position within the organisation or industry. Stakeholders with higher influence and involvement should be given more attention and resources.
Step 3: Assess stakeholder interests and objectives
Understanding stakeholder interests and objectives is crucial for project success. This can be done through interviews, surveys, or other data collection methods. By analysing stakeholders’ needs, expectations, and motivations, project managers can better align project goals and strategies to meet stakeholder requirements.
Step 4: Analyse stakeholder power and dynamics
Analysing stakeholder power and dynamics involves assessing the relationships and interactions between stakeholders. This can be done through stakeholder mapping, where stakeholders are categorised based on their level of influence and impact on the project. Understanding stakeholder power and dynamics helps project managers anticipate potential conflicts, align stakeholder interests, and foster collaboration.
Step 5: Prioritise stakeholders
Prioritising stakeholders involves ranking them based on their level of influence, interest, and potential impact on the project. This helps project managers allocate resources, define communication strategies, and focus on key stakeholders who can significantly impact the project’s success.
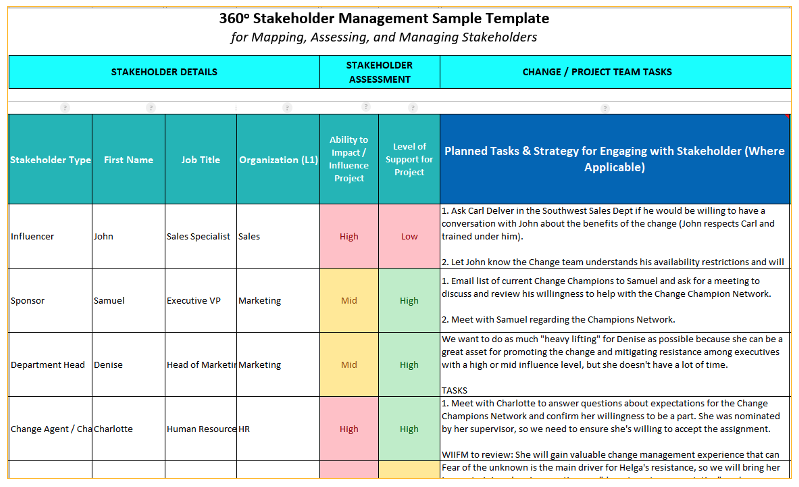
Step 6: Create stakeholder profiles
Creating stakeholder profiles involves documenting information about each stakeholder, such as their role, responsibilities, interests, objectives, and influence. This helps project managers gain a comprehensive understanding of each stakeholder and tailor engagement strategies and communication channels accordingly.
Step 7: Develop stakeholder engagement strategies
Based on the stakeholder analysis, project managers can develop stakeholder engagement strategies. This involves defining communication channels and methods, tailoring engagement approaches for different stakeholders, addressing their concerns and interests, involving them in decision-making, and building trust and rapport.
Tools and Techniques for Stakeholder Analysis
Stakeholder identification matrix
A stakeholder identification matrix is a tool that helps project managers systematically identify stakeholders based on their level of influence and interest in the project. It allows for a comprehensive view of stakeholders and ensures that all relevant stakeholders are considered.
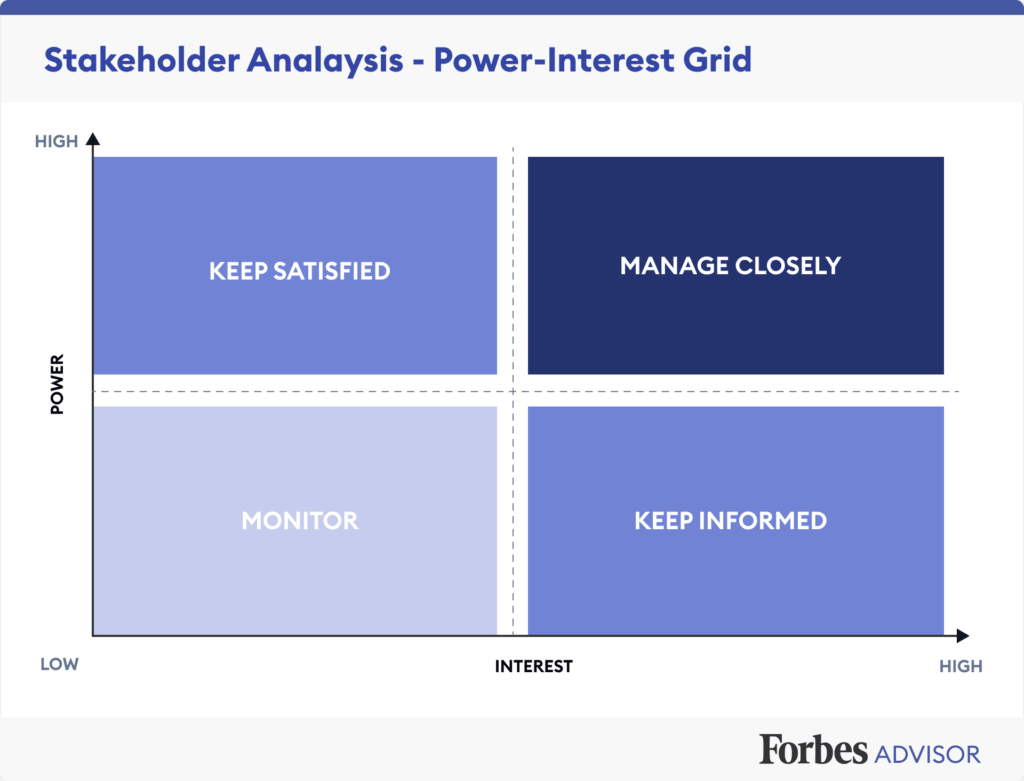
Power-interest grid
The power-interest grid is a visual tool used to analyse stakeholders based on their level of power and interest. It helps project managers prioritise stakeholders and determine appropriate levels of engagement and communication.
Stakeholder prioritisation matrix
A stakeholder prioritisation matrix is a tool that helps project managers rank stakeholders based on their level of influence, interest, and potential impact on the project. It assists in resource allocation, decision-making, and risk management.
Stakeholder influence diagram
A stakeholder influence diagram is a visual representation of the relationships and interactions between stakeholders. It helps project managers analyse stakeholder power, influence, and dynamics and identify potential conflicts or alliances.
Stakeholder mapping
Stakeholder mapping is a technique used to visually represent stakeholders based on their influence and interest in the project. It provides a clear overview of stakeholder relationships and helps project managers understand the stakeholder landscape.
Data Collection for Stakeholder Analysis
Interviews with stakeholders
Interviews with stakeholders are a valuable data collection method for understanding their interests, expectations, and concerns. Structured or semi-structured interviews can be conducted to gather qualitative data and gain insights into stakeholders’ perspectives.
Surveys and questionnaires
Surveys and questionnaires can be used to collect quantitative or qualitative data from stakeholders. They are helpful for gathering feedback, opinions, and preferences on specific project aspects or stakeholder-related issues.
Document analysis
Document analysis involves reviewing relevant documents such as project proposals, contracts, reports, or policies to collect information about stakeholders. It provides insights into stakeholders’ roles, responsibilities, and expectations.
Observation and feedback
Observation and feedback involve observing stakeholders’ behaviours, interactions, or reactions during project meetings, workshops, or events. This provides valuable information about stakeholder engagement, satisfaction levels, and potential conflicts.
Market research and customer analysis
Market research and customer analysis can provide insights into external stakeholders’ perspectives, needs, and preferences. This data can be collected through surveys, focus groups, or online research to better understand customers’ expectations and align project strategies accordingly.
Analysing Stakeholder Interests and Objectives
Identifying stakeholder goals and objectives
Analysing stakeholder interests and objectives involves identifying their goals, motivations, and desired outcomes. This can be done through interviews, surveys, or other data collection methods to gain insights into what stakeholders want to achieve through the project.
Assessing stakeholder expectations
Assessing stakeholder expectations involves understanding what stakeholders expect from the project in terms of deliverables, quality, timelines, and resources. This can be done through discussions, feedback sessions, or using survey tools to gather stakeholder perspectives.
Evaluating stakeholder influence and impact
Evaluating stakeholder influence and impact helps project managers understand the extent to which stakeholders can affect project decisions and outcomes. This analysis can be done through stakeholder mapping, power-interest grids, or other visual tools to assess stakeholder power dynamics.
Identifying potential conflicts and alignments
Analysing stakeholder interests and objectives helps identify potential conflicts or alignments between stakeholders. By understanding their varying expectations and motivations, project managers can proactively address conflicts and find ways to align stakeholder interests to ensure project success.
Prioritising Stakeholders for Effective Management
Assessing stakeholder power vs. interest
Assessing stakeholder power versus interest helps project managers categorise stakeholders into different groups. High power and high interest stakeholders require close management and communication, while low power and low interest stakeholders may require minimal effort.
Categorising stakeholders based on influence
Categorising stakeholders based on their influence allows project managers to prioritise their engagement efforts. This can be done by creating categories such as primary, secondary, influential, or supportive stakeholders, and allocating resources accordingly.
Determining stakeholder significance and impact
Determining stakeholder significance and impact involves assessing the potential effect of stakeholders on the project. This analysis helps project managers focus on stakeholders who can significantly influence project outcomes and allocate resources effectively.
Understanding stakeholder dynamics and relationships
Understanding stakeholder dynamics and relationships is crucial for effective management. By analysing stakeholder interactions, power dynamics, and potential conflicts or alliances, project managers can develop strategies to foster positive relationships, address conflicts, and build a cooperative environment.
Creating Stakeholder Profiles
Gathering information for stakeholder profiles
Gathering information for stakeholder profiles involves collecting data on stakeholders’ roles, responsibilities, interests, influence, and objectives. This information can be obtained through interviews, surveys, document analysis, or feedback sessions.
Identifying key attributes of stakeholders
Identifying key attributes of stakeholders helps project managers gain a comprehensive understanding of each stakeholder. This can include their background, expertise, communication preferences, decision-making authority, and potential conflicts or alignments with other stakeholders.
Documenting stakeholder characteristics
Documenting stakeholder characteristics helps project managers create comprehensive stakeholder profiles. These profiles can include information such as stakeholder roles, goals, motivations, preferred communication channels, and potential risks or concerns.
Creating stakeholder engagement plans
Using the stakeholder profiles, project managers can develop stakeholder engagement plans that outline the strategies, communication channels, and activities for effectively engaging with each stakeholder. These plans help ensure that stakeholders receive the right information at the right time and are involved in project decision-making.
Developing Stakeholder Engagement Strategies
Defining communication channels and methods
Defining communication channels and methods involves selecting the most appropriate ways to communicate and engage with stakeholders. This can include face-to-face meetings, emails, project newsletters, social media platforms, or online collaboration tools.
Tailoring engagement strategies for different stakeholders
Each stakeholder has unique characteristics and preferences. Tailoring engagement strategies involves adapting the communication approach, frequency of updates, and level of involvement based on stakeholders’ needs, interests, and communication styles.
Addressing stakeholder concerns and interests
Addressing stakeholder concerns and interests is vital for maintaining positive stakeholder relationships. By actively listening and seeking to understand stakeholders’ perspectives, project managers can address their concerns, provide necessary information, and find ways to meet their interests.
Involving stakeholders in decision-making
Involving stakeholders in decision-making processes fosters a sense of ownership and increases stakeholder commitment. It allows stakeholders to contribute their expertise, perspectives, and insights, leading to better decision outcomes and increased stakeholder satisfaction.
Building trust and rapport with stakeholders
Building trust and rapport with stakeholders is crucial for effective stakeholder engagement. This can be done by being transparent, consistent, and reliable in communication, delivering on commitments, and actively listening to stakeholder feedback and concerns.
Applying Stakeholder Analysis in Project Management
Integrating stakeholder analysis with project planning
Integrating stakeholder analysis with project planning ensures that stakeholders’ needs, expectations, and perspectives are considered from the beginning. By involving stakeholders in the planning process and aligning project goals with stakeholder interests, project managers can increase the chances of project success.
Utilising stakeholder analysis for risk management
Stakeholder analysis helps identify potential risks associated with stakeholders. By understanding their interests, influence, and potential conflicts, project managers can proactively address risks and find ways to mitigate their impact. This allows for better risk management and reduces the likelihood of project disruptions.
Incorporating stakeholder feedback in project execution
Incorporating stakeholder feedback in project execution is essential for meeting their expectations and ensuring project success. By regularly seeking feedback, project managers can make adjustments, address issues, and improve project outcomes based on stakeholder input.
Measuring stakeholder satisfaction and success
Measuring stakeholder satisfaction and success involves evaluating stakeholders’ perception of the project’s outcomes and their level of satisfaction with the project process. This can be done through surveys, feedback sessions, or other assessment methods to gauge stakeholder satisfaction and identify areas for improvement.
Continuously adapting stakeholder engagement strategies
Stakeholder engagement strategies should be flexible and adaptable throughout the project life cycle. By monitoring stakeholder dynamics, needs, and interests, project managers can make necessary adjustments to their engagement strategies and ensure ongoing stakeholder satisfaction and support.
In conclusion, conducting a stakeholder analysis is crucial for project success. By understanding the needs, expectations, and concerns of various stakeholders, project managers can effectively plan, execute, and manage projects. Through tools and techniques like stakeholder identification, power-interest grids, and stakeholder mapping, project managers can gather and analyse relevant stakeholder data. This data, collected through interviews, surveys, or other methods, helps project managers create stakeholder profiles and develop tailored engagement strategies. By incorporating stakeholder analysis in project management, project managers can align project goals with stakeholder interests, mitigate risks, and foster positive stakeholder relationships.
