How to do a SWOT analysis
How to do a SWOT analysis
Are you looking to enhance your project management skills? If so, understanding how to perform a SWOT analysis can be a game-changer. In this article, we will dive into the world of project management and explore the importance of conducting a SWOT analysis. By leveraging this powerful tool, you will be able to assess the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats associated with your project, ultimately boosting your ability to make informed decisions and drive success. So, let’s get started on this exciting journey of project management excellence!
Speak to MCTC today about our consultancy advice and training packages.
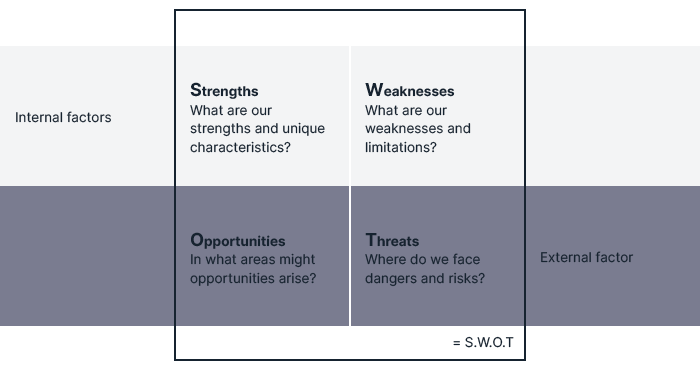
Understanding SWOT Analysis
Definition of SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool that helps project managers assess and evaluate the internal and external factors that can impact the success of a project. SWOT stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. By identifying and analysing these factors, project managers can make informed decisions and develop action plans to mitigate risks and leverage opportunities.
Purpose of SWOT Analysis
The main purpose of conducting a SWOT analysis is to gain a comprehensive understanding of the project’s current state and the external environment in which it operates. By identifying the strengths and weaknesses of the project internally and the opportunities and threats externally, project managers can determine the best course of action for achieving project objectives. SWOT analysis enables project managers to develop strategies that utilise their strengths, address weaknesses, capitalise on opportunities, and mitigate potential threats.
Preparing for the SWOT Analysis
Choose a Project
Before conducting a SWOT analysis, it is essential to choose a specific project or initiative to focus on. Selecting a project that requires strategic decision-making can help project managers identify and evaluate factors that can impact its success. By narrowing down the scope of the analysis to a specific project, project managers can better understand the project’s unique characteristics and tailor the SWOT analysis accordingly.
Gather Relevant Information
To conduct an effective SWOT analysis, project managers need to gather relevant information about the project and its external environment. This includes collecting data on the project’s objectives, timeline, budget, and resources. Additionally, project managers need to research market trends, competitor strategies, and any regulatory or legal factors that could affect the project’s outcomes. The more comprehensive the information gathered, the more accurate and valuable the SWOT analysis will be.
Assemble a Project Management Team
A SWOT analysis is a collaborative effort, requiring input from various stakeholders to ensure a comprehensive and well-rounded evaluation. Assemble a project management team consisting of individuals with diverse expertise and perspectives. This team can include project managers, subject matter experts, team leaders, and other key stakeholders. By involving a cross-functional team, project managers can gain valuable insights and different perspectives, enhancing the accuracy and effectiveness of the SWOT analysis.
Strengths: Internal Analysis
Identify Unique Competencies
In the strengths analysis phase of the SWOT analysis, project managers focus on identifying the unique competencies and advantages that the project possesses. These can be specific skills, technologies, or resources that give the project a competitive edge. By identifying these strengths, project managers can leverage them to maximise project success. For example, if a project has a team with expertise in a particular technology, it can be advantageous in delivering innovative solutions.
Assess Team Skills and Expertise
An essential aspect of the internal analysis is assessing the skills and expertise of the project team. Identifying the strengths and weaknesses of the team members allows project managers to allocate tasks effectively and ensure that the right people are in the right roles. This assessment can also help identify any skill gaps that need to be addressed through training or recruiting. By building a strong and skilled team, project managers can enhance the project’s chances of success.
Evaluate Available Resources
During the internal analysis, project managers evaluate the resources available to the project. This includes assessing the project’s budget, physical assets, technology, and any other resources required for successful project execution. Understanding the availability and limitations of resources helps project managers plan and allocate them efficiently. By leveraging available resources effectively, project managers can optimise project outcomes.
Weaknesses: Internal Analysis
Identify Skill Gaps
In the weaknesses analysis phase, project managers focus on identifying the skill gaps and deficiencies within the project team. This includes identifying areas where the team lacks expertise or experiences limitations. By recognising these weaknesses, project managers can develop strategies to address skill gaps. This may involve training team members, bringing in external experts, or reallocating resources to overcome weaknesses and enhance the project’s performance.
Assess Limitations and Constraints
Within the internal analysis, project managers assess the limitations and constraints that may impact the project’s success. These limitations can include budget constraints, time restrictions, or physical resource shortages. By acknowledging these limitations, project managers can develop realistic plans that take into account the project’s constraints. This involves setting achievable goals and managing stakeholders’ expectations accordingly.
Evaluate Internal Barriers
Internal barriers can pose significant challenges to project success. During the SWOT analysis, project managers identify any internal barriers that may hinder progress or impede the project’s objectives. These barriers could include resistance to change, lack of communication between team members, or inefficient processes. By recognising and addressing these barriers, project managers can create a supportive environment that fosters collaboration and maximises project outcomes.
Opportunities: External Analysis
Identify Market Trends and Conditions
In the external analysis phase, project managers focus on identifying market trends and conditions that present opportunities for the project. This includes researching industry trends, customer demands, and emerging technologies. By understanding market dynamics, project managers can identify opportunities to innovate, expand, or adjust project strategies to align with market needs. Leveraging market trends and conditions can give the project a competitive advantage and increase its chances of success.
Analyse Competitor Strategies
Understanding competitor strategies is crucial for identifying potential opportunities in the external environment. By analysing competitor strengths and weaknesses, project managers can identify gaps or areas for improvement. This analysis helps project managers develop strategies that differentiate their project and capitalise on market gaps. By staying ahead of competitors, project managers can position the project for success.
Assess Potential Collaborations
During the external analysis, project managers assess potential collaborations and partnerships that can enhance the project’s outcomes. This includes identifying potential stakeholders, strategic alliances, or suppliers who can contribute expertise, resources, or market access. By forming collaborations, project managers can leverage external capabilities and tap into new markets or audiences. Collaboration can open doors to new opportunities and increase the project’s chances of success.
Threats: External Analysis
Identify Potential Obstacles
In the external analysis phase, project managers identify potential obstacles that can pose threats to the project’s success. This includes recognising challenges such as economic downturns, political instability, or evolving customer preferences. By anticipating these obstacles, project managers can develop contingency plans and strategies to mitigate their impact. Being proactive in identifying threats allows project managers to adapt and respond effectively to changing external conditions.
Evaluate Regulatory and Legal Factors
Regulatory and legal factors can significantly impact project outcomes. During the SWOT analysis, project managers evaluate any regulatory or legal factors that may pose threats to the project. This includes considering compliance requirements, licenses, permits, and industry regulations. By understanding and complying with relevant regulations, project managers can minimise legal risks and ensure project success.
Assess Market Risks
Market risks, such as changes in demand, emerging competitors, or disruptive technologies, can pose threats to the project’s success. In the external analysis, project managers assess these risks and evaluate their potential impact on the project. By anticipating market risks, project managers can develop strategies to mitigate their effects or exploit market shifts. Assessing market risks enables project managers to proactively navigate uncertain environments and protect the project’s interests.
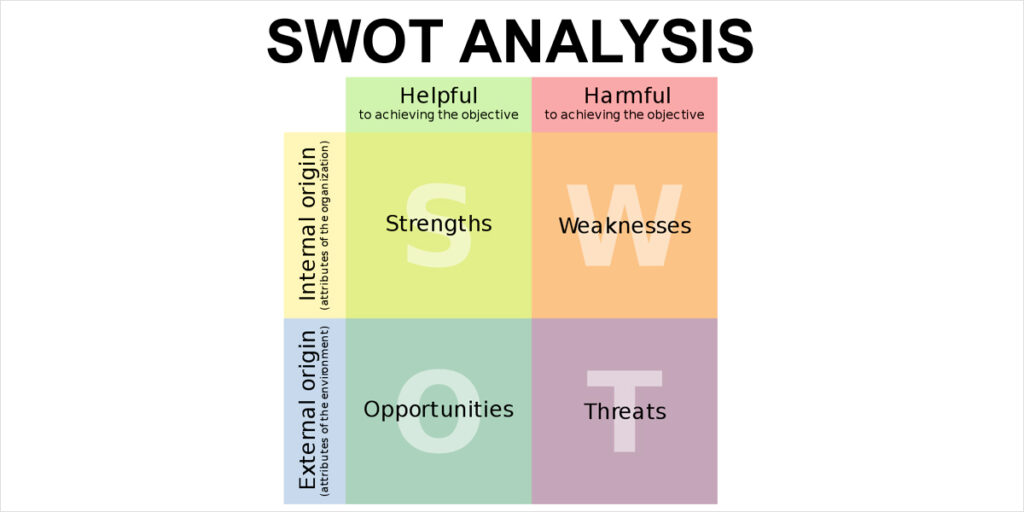
Analysing and Evaluating SWOT Factors
Prioritising Strengths
After conducting the SWOT analysis, project managers need to analyse and evaluate the identified factors. When it comes to strengths, project managers should prioritise those that provide the most significant competitive advantages or unique capabilities. By focusing on these strengths, project managers can develop strategies that leverage their most valuable assets and differentiate the project from competitors.
Mitigating Weaknesses
To mitigate weaknesses, project managers need to develop action plans that address skill gaps, limitations, and internal barriers. This may involve training programs, process improvements, or resource reallocation. By addressing weaknesses, project managers can minimise their impact on the project’s success and optimise team performance.
Leveraging Opportunities
To leverage opportunities, project managers need to develop strategies that capitalise on market trends, competitor gaps, and potential collaborations. This may involve adapting project objectives, refining product offerings, or forming strategic alliances. By effectively leveraging opportunities, project managers can position the project for growth and success.
Managing Threats
To manage threats, project managers need to develop contingency plans and risk mitigation strategies. This includes creating alternative scenarios, establishing early warning systems, and building resilience into project plans. By effectively managing threats, project managers can minimise their impact and safeguard project outcomes.
Utilising SWOT Analysis in Project Management
Informing Decision-Making
SWOT analysis provides valuable insights that inform decision-making in project management. By understanding the project’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, project managers can make informed choices about resource allocation, project strategies, and risk mitigation. SWOT analysis acts as a decision-making tool that ensures project managers consider all relevant factors before taking action.
Identifying Project Risks
SWOT analysis helps identify project risks by examining both internal and external factors that can impact the project’s success. By assessing weaknesses and external threats, project managers can identify potential risks and develop strategies to mitigate them. This proactive approach to risk identification allows project managers to create contingency plans and minimise the likelihood and impact of potential risks.
Developing Action Plans
SWOT analysis guides project managers in developing action plans that align with project objectives and leverage strengths. By taking the insights gained from the analysis, project managers can develop strategies and initiatives that address weaknesses, capitalise on opportunities, and manage threats. These action plans provide a road map for project execution and ensure that resources and efforts are focused on areas that will drive project success.
Integrating SWOT Analysis with Project Methodologies
Agile Project Management
In Agile project management, SWOT analysis can be integrated into the sprint planning process. By conducting a SWOT analysis at the beginning of each sprint, project managers can identify and prioritise strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats specific to that sprint’s goals. This allows the team to adapt their strategies and actions throughout the project to optimise performance and meet project objectives.
Waterfall Project Management
In Waterfall project management, SWOT analysis can be incorporated during the project initiation phase. By conducting a comprehensive SWOT analysis at the beginning of the project, project managers can identify and address potential risks, allocate resources effectively, and inform project planning. This ensures that the project is set up for success from the start and reduces the likelihood of unforeseen obstacles derailing the project.
Programme Management
Programme managers can utilise SWOT analysis to assess the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of multiple projects within a program. By conducting an integrated SWOT analysis across projects, programme managers can identify synergies, dependencies, and risks that affect the overall program’s success. This allows programme managers to make informed decisions and allocate resources strategically to maximise program outcomes.
Conclusion
SWOT analysis is a valuable tool in project management that helps project managers gain a comprehensive understanding of the internal and external factors impacting a project. By conducting a thorough analysis of strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, project managers can develop strategies, allocate resources effectively, and make informed decisions. SWOT analysis guides project managers in identifying and mitigating risks, leveraging opportunities, and aligning project objectives with organisational goals. By integrating SWOT analysis with project management methodologies, project managers can optimise project outcomes and increase the chances of project success.