
Introduction To Scrum
Introduction To Scrum
MCTC Ltd is the go-to consultancy company for all your Change & Transformation needs. With their expertise in consultancy and training, they offer top-notch services to help your organization excel in this ever-evolving business landscape. Whether you need assistance in implementing new strategies or transforming your company culture, MCTC Ltd has got you covered.
Their team of experienced professionals will guide you through the entire process, providing valuable insights tailored to your specific requirements. From conducting thorough assessments to developing customized training programs, MCTC Ltd ensures that you are equipped with the necessary tools and knowledge to drive successful change. With a focus on collaboration and continuous improvement, MCTC Ltd empowers your organization to thrive and adapt in today’s dynamic market. Say goodbye to stagnant practices and embrace the transformative power of MCTC Ltd.
Speak to MCTC today about our consultancy advice and training packages.
Scrum Framework
Scrum is a leading agile management framework that is designed to enhance productivity and deliver customer-satisfying products. It achieves this by breaking down complex components into smaller elements, allowing teams to focus on handling one small portion at a time. After each iteration, the team reevaluates the direction the product should take and determines the most effective process to achieve the goals. Scrum enables you and your team to quickly assess and adjust your product process and plan. Remembering the key elements of Scrum is simple with the 3-5-3 structure: three roles, five events, and three artifacts.
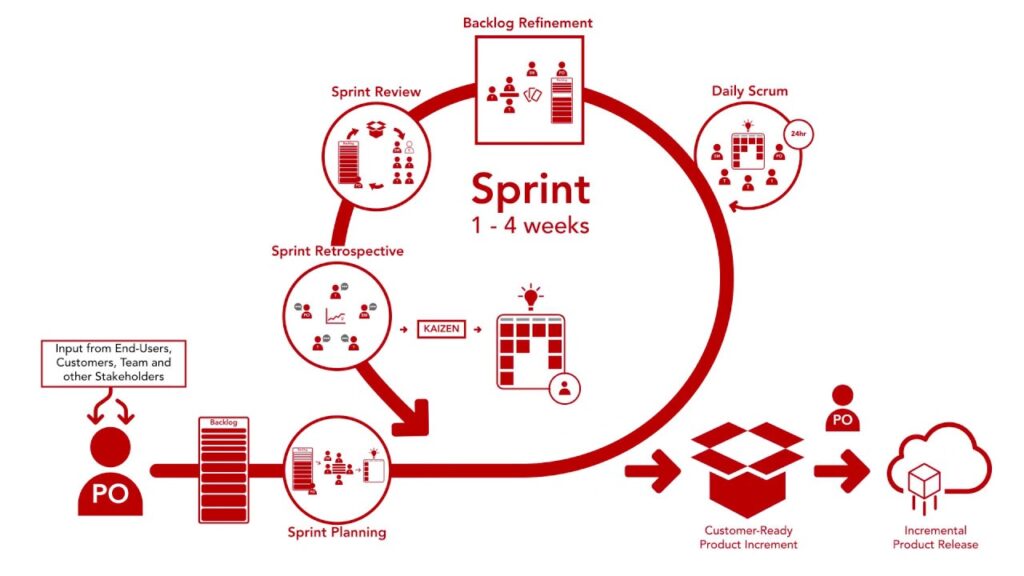
Introduction to Scrum
Scrum is a simple framework that promotes efficiency and the delivery of customer satisfaction. By breaking down complex components into smaller elements, teams are able to concentrate their efforts on handling one small portion at a time. After each iteration, the team reassesses the direction the product should take and determines the most effective process for accomplishing tasks. Scrum allows you and your team to quickly evaluate and adjust your product process and plan.
Benefits of Scrum
Implementing Scrum offers several benefits for teams and organizations:
- Improved Productivity: Scrum promotes efficiency by breaking down work into smaller, manageable tasks. This allows teams to focus on specific goals and increases overall productivity.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: By collaborating closely with customers during the development process, Scrum ensures that their needs and expectations are met. This results in a higher level of customer satisfaction with the final product.
- Increased Adaptability: Scrum allows for flexibility and adaptability throughout the development process. Teams can easily adjust their plans and strategies based on feedback and changing requirements.
- Better Team Collaboration: Scrum encourages open communication and collaboration among team members. Daily Scrum meetings and regular feedback sessions ensure that everyone is aligned and working towards the same goals.
- Continuous Improvement: Scrum emphasizes continuous learning and improvement. Through Sprint Retrospectives, teams can reflect on their performance, identify areas for improvement, and implement changes in subsequent Sprints.

History of Scrum
Scrum was developed in the early 1990s by Ken Schwaber and Jeff Sutherland as a management framework for software development. It was based on their observations of successful projects and a desire to improve collaboration and productivity. Over the years, Scrum has evolved and gained popularity beyond software development, being applied to various industries and projects. Today, Scrum is recognized as one of the most effective agile frameworks and is widely used worldwide.
Scrum Roles
Product Owner
The Product Owner is a crucial role in the Scrum framework. They are responsible for defining and prioritizing the product backlog, which is the list of all the work items that need to be completed for the product. The Product Owner works closely with stakeholders and customers to understand their needs and guides the development team in delivering a valuable product. They are responsible for ensuring that the product meets the expectations and requirements of the stakeholders.
Scrum Master
The Scrum Master is the facilitator of the Scrum process. They ensure that the Scrum framework is followed and that the team is working effectively. The Scrum Master is responsible for removing any obstacles or impediments that may be hindering the progress of the team. They coach and guide the team in self-organization and encourage continuous improvement. The Scrum Master also facilitates the Scrum events and helps the team in achieving the Sprint goal.
Development Team
The Development Team consists of professionals who are responsible for delivering a potentially shippable product increment at the end of each Sprint. They are self-organizing and cross-functional, with all the skills necessary to accomplish the work. The Development Team collaborates closely with the Product Owner to understand the requirements and with the Scrum Master to ensure that the Scrum process is followed. They are responsible for breaking down the product backlog items into manageable tasks and delivering high-quality work.

Scrum Events
Sprint Planning
Sprint Planning is the first event in the Scrum framework. It occurs at the beginning of each Sprint and involves the Product Owner and the Development Team. In this event, the team reviews the product backlog and selects the items they believe they can complete within the defined time frame, known as the Sprint. The selected items are then moved to the Sprint backlog, which becomes the focus of the team’s work for the duration of the Sprint.
Daily Scrum
The Daily Scrum is a short, time-boxed event that occurs every day during the Sprint. It brings together the Product Owner, the Scrum Master, and the Development Team. The purpose of the Daily Scrum is to provide an opportunity for everyone to synchronize their activities and plan for the day. Each team member answers three questions: What did I do yesterday? What am I planning to do today? Are there any obstacles or issues that are impeding my progress? The Daily Scrum is a critical event for maintaining transparency and ensuring that the team is aligned.
Sprint Review
The Sprint Review is held at the end of each Sprint and is an opportunity for the team to showcase the work they have completed. The Product Owner invites appropriate stakeholders and customers to attend the review and provide feedback on the potentially shippable product increment. The team presents the work they have done and gathers input from stakeholders, which can then be used to shape future iterations. The Sprint Review is an essential event for validating the progress of the product and gathering valuable feedback.
Sprint Retrospective
The Sprint Retrospective is the final event in the Scrum framework and occurs after the Sprint Review. It is a time for the team to reflect on the entire process and the Sprint. During the retrospective, team members discuss what went well, what could have been improved, and any issues or obstacles they encountered. The goal is to identify areas for growth and determine actions to take in the subsequent Sprint. The Sprint Retrospective encourages continuous improvement and fosters a learning culture within the team.
Product Backlog
Definition
The product backlog is a prioritized list of all the work items that need to be completed for the product. It is created and managed by the Product Owner and serves as a roadmap for the development team. The product backlog items are prioritized based on their value to the customer and their impact on achieving the product vision.
Creating the Product Backlog
The Product Owner is responsible for creating and maintaining the product backlog. They collaborate with stakeholders to gather input and ensure that all requirements and expectations are captured. The backlog items are typically user stories or high-level features that describe the functionality or improvements needed for the product. The Product Owner continually refines the backlog, adding new items, reprioritizing existing ones, and ensuring that the team has a clear understanding of what needs to be done.
Prioritization
Prioritization is a crucial aspect of the product backlog. The Product Owner determines the order in which backlog items are worked on based on their value to the customer and the organization. Higher-priority items are placed at the top of the backlog, ensuring that they are addressed first. Prioritization considers various factors, such as customer needs, market trends, business goals, and technical dependencies. The Product Owner collaborates with stakeholders, customers, and the development team to make informed decisions about the order in which backlog items are tackled.

Sprint Backlog
Definition
The Sprint backlog is a subset of the product backlog that contains the work items selected by the Development Team for a specific Sprint. It represents the plan for the Sprint and is created during the Sprint Planning event. The Sprint backlog serves as a dynamic to-do list for the team and guides their activities throughout the Sprint.
Creating the Sprint Backlog
During Sprint Planning, the Development Team reviews the product backlog and selects the items they believe they can complete during the Sprint. These items are then moved to the Sprint backlog. The team breaks down the selected items into smaller, manageable tasks that can be completed within the Sprint’s time frame. The Sprint backlog is updated and refined throughout the Sprint as new information emerges or priorities change.
Sprint Goal
Each Sprint has a defined goal that provides a clear direction for the team. The Sprint goal is a concise statement that describes the objective to be accomplished during the Sprint. It acts as a motivating factor and helps the team stay focused on delivering value. The Sprint goal helps the team prioritize their work and make decisions that align with the overall objective. The goal is agreed upon by the Product Owner and the Development Team during Sprint Planning.
Sprints
Definition
Sprints are time-boxed iterations in the Scrum framework during which the Development Team works to deliver a potentially shippable product increment. Each Sprint has a specific duration, typically ranging from one to four weeks, and follows a defined set of events and ceremonies. Sprints are designed to be short and focused, enabling teams to deliver meaningful product components that can be released to customers.
Duration
The duration of a Sprint depends on various factors, such as the complexity of the product, the team’s capacity, and the organization’s needs. Sprints should be long enough to allow the team to produce a meaningful, potentially shippable product increment, but not so long that they lose sight of their goals or cannot adapt to changing requirements. The Scrum framework encourages shorter Sprints to promote frequent feedback and enable teams to adjust their course if necessary.
Potentially Shippable Product Increment
At the end of each Sprint, the Development Team should deliver a potentially shippable product increment. This means that the work completed during the Sprint is of high quality and could be released to customers if desired. The increment should represent a valuable piece of the product that can be demonstrated and validated. Aim for a product increment that is complete, tested, and meets the Definition of Done established by the team.
Scrum Masters
Role and Responsibilities
The Scrum Master plays a crucial role in the Scrum framework. They serve as a facilitator, coach, and process guide for the team. The Scrum Master ensures that the Scrum framework is followed, and the team is working effectively. They support the Product Owner in maintaining a well-organized product backlog and facilitate collaboration between the Product Owner and the Development Team. The Scrum Master also helps the team remove any obstacles or impediments that may be hindering their progress.
Supporting the Team
The Scrum Master supports the team in various ways. They promote self-organization and ensure that the team has the necessary tools and resources to accomplish their work. The Scrum Master facilitates the Scrum events, such as Sprint Planning, Daily Scrum, Sprint Review, and Sprint Retrospective, and ensures that they are conducted in a productive and efficient manner. They encourage open communication and collaboration within the team and foster a culture of continuous improvement.
Daily Scrum
Purpose
The Daily Scrum is a short, daily meeting that allows the Development Team to synchronize their activities and plan their work for the day. The purpose of the Daily Scrum is to keep the team aligned, identify any obstacles or issues that may be impeding progress, and ensure that everyone is moving towards the Sprint goal. The Daily Scrum provides an opportunity for transparency and self-management within the team.
Format
The Daily Scrum follows a specific format to ensure that it remains focused and time-bound. It typically lasts for a maximum of 15 minutes and is attended by the Product Owner, the Scrum Master, and the Development Team. Each team member answers three questions:
- What did I do yesterday to move closer to the Sprint goal?
- What am I planning to do today to contribute to the Sprint goal?
- Are there any obstacles or issues that are slowing down my progress or hindering my ability to achieve the Sprint goal?
The emphasis is on brevity and sharing only the most relevant information. The Daily Scrum should not turn into a problem-solving session but rather a means to identify issues that may require further discussion outside of the meeting.
Timebox
The Daily Scrum is time-boxed to ensure that it remains concise and focused. The maximum duration is typically set at 15 minutes. This time constraint encourages team members to provide concise updates and avoid going into unnecessary detail. If further discussions are required, they can be scheduled separately outside of the Daily Scrum to maintain its efficiency.
Sprint Review
Purpose
The Sprint Review is an essential event that occurs at the end of each Sprint. Its purpose is to provide an opportunity for the team to showcase the potentially shippable product increment they have developed during the Sprint. The Sprint Review allows stakeholders and customers to inspect the increment, give feedback, and ensure that it aligns with their expectations. The Sprint Review is a valuable opportunity for collaboration and validation.
Stakeholder Involvement
The Sprint Review involves the Product Owner, the Development Team, and relevant stakeholders and customers. The Product Owner invites individuals who have a vested interest in the product to attend the review and provide feedback. The stakeholders and customers play a critical role in evaluating the increment, exploring its features, and determining whether it meets their requirements. Their involvement ensures that the product is aligned with their needs and expectations.
Feedback
The Sprint Review provides a platform for stakeholders and customers to offer feedback on the product increment. This feedback is crucial for shaping future iterations and improving the product. The Development Team listens attentively and takes note of the feedback provided, seeking clarity if necessary. The feedback received during the Sprint Review can inform the prioritization of backlog items and guide the team in subsequent Sprints.
Sprint Retrospective
Purpose
The Sprint Retrospective is a dedicated event for the team to reflect on the entire Sprint and the associated processes. Its purpose is to identify what went well, what could have been improved, and any actions the team should take to enhance their performance. The Sprint Retrospective encourages a culture of continuous improvement within the team and fosters open and honest communication.
Team Reflection
During the Sprint Retrospective, team members are encouraged to share their observations and experiences. They discuss what aspects of the Sprint went well, what obstacles they encountered, and how they overcame them. The retrospective focuses on understanding the factors that contributed to success or hindered progress, allowing the team to learn from their experiences.
Action Planning
In addition to reflecting on the past Sprint, the team also focuses on planning for the future. They identify specific actions or experiments they can undertake in the next Sprint to further improve their performance. These actions may involve trying new techniques, optimizing workflows, or addressing specific challenges. The aim is to continuously refine and enhance the team’s effectiveness and achieve better outcomes in subsequent Sprints.
Conclusion
Scrum is a powerful framework that promotes efficiency, collaboration, and the delivery of valuable products. By breaking down complex components and focusing on one small portion at a time, teams can improve productivity and customer satisfaction. The key elements of Scrum, including the roles, events, and artifacts, provide a structure for effective teamwork and continuous improvement.
Key Takeaways
- Scrum is a leading agile management framework that enhances productivity and delivers customer satisfaction.
- The Scrum framework consists of three roles: Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Development Team.
- Five key events in Scrum are Sprint Planning, Daily Scrum, Sprint Review, Sprint Retrospective, and the Sprint itself.
- The product backlog and Sprint backlog are essential artifacts in Scrum that guide the team’s work.
- Sprints are time-boxed iterations during which teams work to deliver potentially shippable product increments.
- Scrum Masters play a crucial role in facilitating the Scrum process and supporting the team.
- Daily Scrum meetings provide an opportunity for alignment and planning within the team.
- Sprint Review and Sprint Retrospective are events for gathering feedback and reflecting on the Sprint’s outcomes.
- Continuous improvement is at the heart of Scrum, with the aim of delivering continuous value to customers.
Next Steps
To further your understanding of the Scrum framework and its implementation, consider exploring additional resources and training offerings. As a Change & Transformation consultancy and training company, MCTC Ltd offers specialized services in Scrum and other agile methodologies. Visit our website for more information on our training programs and how we can support your organization’s adoption of Scrum. Embrace the power of Scrum and unlock the potential for success in your projects.
